Check valves are essential components in piping systems that allow fluid to flow in one direction while preventing reverse flow. Among the various types of check valves, lift check valves and piston check valves are two of the most commonly used designs in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. While they share a similar operating principle, their construction and performance characteristics differ in several ways.
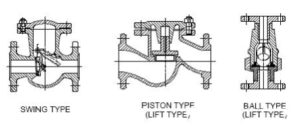
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Working Principle
Lift Check Valve
A lift check valve operates much like a globe valve without the handwheel. When the fluid flows in the forward direction, the pressure lifts the disc (or ball) off the seat, allowing flow to pass through. When the flow stops or reverses, gravity and reverse pressure push the disc back onto the seat, preventing backflow.
The disc moves vertically (up and down) in response to the flow.
Ideal for high-velocity applications and clean fluids.
Piston Check Valve
A piston check valve works on the same basic lift principle but includes a guided piston instead of a loose disc. The piston slides within a cylinder and is often assisted by a spring to return it to the closed position when pressure drops or reverses.
The piston movement is linear and guided, providing more controlled operation.
The spring ensures quicker closure, preventing water hammer and reverse flow surges.
2. Structural Differences
| Feature | Lift Check Valve | Piston Check Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Closing Element | Disc or Ball | Piston (with guide and spring) |
| Guiding Mechanism | Limited or none | Fully guided piston movement |
| Spring Mechanism | Usually absent | Typically includes a spring for assisted closure |
| Design Similarity | Resembles a Globe Valve | Resembles a Globe Valve with additional piston chamber |
| Sealing | Metal-to-metal or soft seat | Metal-to-metal, often tighter seal |
3. Performance Characteristics
Response Speed:
Piston check valves close faster due to the spring mechanism, reducing the risk of water hammer. Lift check valves rely mainly on gravity and reverse flow pressure, so they react slightly slower.Leak Tightness:
The guided piston provides a more uniform seating and tighter seal, especially under high pressure.Maintenance:
Lift check valves are simpler and easier to maintain due to fewer components. Piston check valves, while offering better performance, require more precise maintenance because of the spring and piston guide system.Pressure Range:
Both types can handle high-pressure systems, but piston check valves are preferred for cyclic or pulsating flow conditions where stability and quick response are important.
4. Application Differences
| Application | Lift Check Valve | Piston Check Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Medium Type | Clean liquids, steam, and gases | Steam, condensate, high-pressure fluids |
| Orientation | Typically installed in horizontal lines | Can be installed horizontally or vertically |
| Flow Conditions | Steady flow | Pulsating or high-pressure flow |
| Industries | Water supply, chemical processing | Power plants, steam systems, oil & gas, refineries |
5. Advantages and Disadvantages
Lift Check Valve
Advantages:
Simple design, low maintenance
Cost-effective for standard flow conditions
Reliable for clean fluids
Disadvantages:
Not ideal for viscous or slurry media
May close slowly and cause minor backflow
Horizontal installation preferred
Piston Check Valve
Advantages:
Fast closure prevents water hammer
Better sealing and stability under high pressure
Works well with pulsating flow
Disadvantages:
More complex structure and costlier
Requires periodic spring inspection or replacement
6. Summary Table
| Aspect | Lift Check Valve | Piston Check Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Movement | Vertical lift | Guided piston lift |
| Closing Force | Gravity and back pressure | Spring-assisted |
| Sealing Performance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Water Hammer Protection | Limited | Very good |
| Maintenance | Simple | More complex |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
7. Conclusion
Both lift check valves and piston check valves serve the same fundamental purpose—preventing reverse flow—but they excel in different environments.
Choose a lift check valve for general-purpose applications with clean fluids and steady flow.
Opt for a piston check valve in high-pressure, high-temperature, or pulsating systems where tight sealing and rapid response are crucial.
In modern industrial systems, the piston check valve’s enhanced performance often justifies its higher cost, especially where reliability and safety are top priorities.