Water shut-off valves are essential components in residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing systems. Their main purpose is to control, isolate, or stop the flow of water during maintenance, repair, emergencies, or equipment replacement.
Because different applications require different types of valves, understanding each type is important for correct selection and long-term reliability.
This guide explains the most common types of water shut-off valves, their features, advantages, and best applications.

Table of Contents
Toggle1. Ball Valve
Best for: Main water lines, high-pressure systems, full-bore flow
A ball valve uses a spherical ball with a hole through the center.
Turning the handle 90 degrees opens or closes the valve completely.
Features:
Quarter-turn operation
Full port (no flow reduction)
Very reliable and leak-proof
Long service life
Applications:
Main residential shut-off valve
Commercial and industrial water systems
Irrigation, HVAC, well systems
2. Gate Valve
Best for: Low-flow resistance and infrequent operation
A gate valve uses a rising or non-rising metal gate that moves up and down.
Features:
Designed for fully open or fully closed use—not throttling
Smooth, low-resistance flow
Older homes often use gate valves
Applications:
Water mains
Outdoor water supply lines
Underground systems
Gate valves are reliable but prone to internal corrosion if not operated regularly.
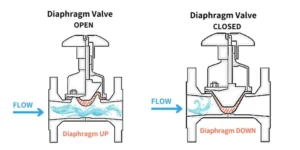
3. Globe Valve
Best for: Throttling and flow regulation
A globe valve uses a movable plug/disc and a stationary ring seat.
Features:
Precise flow control
Higher pressure drop than ball or gate valves
Strong sealing ability
Applications:
Water heaters
Commercial plumbing
Systems requiring flow adjustment
4. Angle Stop Valve
Best for: Under-sink and toilet supply connections
Angle stop valves (angle valves) are compact shut-off valves installed at fixtures.
Features:
90-degree bend
Control water to individual fixtures
Usually compression, threaded, or push-fit types
Applications:
Toilets
Faucets
Under-counter water appliances
5. Straight Stop Valve
Best for: Inline fixture shut-off
Similar to angle stops but with straight-through flow.
Applications:
When plumbing enters directly in-line with the fixture
6. Compression Shut-Off Valve
Best for: Quick installation on copper or CPVC pipe
Installed using a compression nut and ferrule—no soldering required.
Features:
Easy to install
Leak-proof with proper tightening
Applications:
Sinks
Toilets
Small appliances
7. Push-Fit (Push-to-Connect) Valve
Best for: DIY installations and emergency repairs
Brands like SharkBite use push-fit connections.
Features:
No tools or soldering
Works with PEX, copper, and CPVC
Ideal for quick fixes
8. Stop-and-Waste Valve
Best for: Outdoor irrigation and winterizing systems
Allows draining water from the line when closed.
Features:
Prevents freezing damage
Used in yards, gardens, and seasonal buildings
9. Pressure Reducing Valve (PRV)
Best for: High-pressure water systems
Although not a traditional “shut-off” valve, PRVs regulate high inlet pressure and protect plumbing fixtures.
Features:
Adjustable pressure
Installed after the main meter
10. Solenoid Shut-Off Valve
Best for: Automatic leakage protection and smart water systems
Electrically controlled valve that closes automatically.
Features:
Used in smart home water leak systems
Remote or sensor-based shut-off
Applications:
Water leak detectors
HVAC systems
Commercial machinery
11. Automatic Excess Flow Shut-Off Valve
Best for: Emergency protection
Designed to close automatically when it detects abnormally high flow, such as from a burst pipe.
12. Multi-Turn vs Quarter-Turn Valves
| Valve Type | Operation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Quarter-turn | Fast 90° turn | Ball valve, angle stop |
| Multi-turn | Several rotations | Gate valve, globe valve |
Quarter-turn valves are more modern and reliable, while multi-turn valves allow finer control but wear out faster.
How to Choose the Right Water Shut-Off Valve
Consider these factors:
Pipe size and material (PEX, copper, CPVC, steel)
Pressure and temperature levels
Need for manual vs automatic shut-off
Space restrictions
Flow requirements (full port vs reduced port)
Maintenance accessibility
Conclusion
Water shut-off valves range from simple under-sink stop valves to highly engineered solenoid and PRV systems. Selecting the right type ensures safety, reliable operation, and long-term performance in any plumbing system.