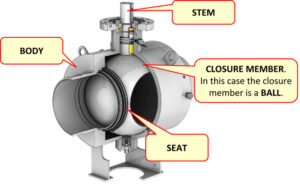
If the valve body is the skeleton of a butterfly valve, the seat is its heart. The ability of a butterfly valve to achieve a “bubble-tight” seal depends entirely on the interference between the disc and the seat material. However, there is no “universal” material.

Choosing the wrong seat material can lead to swelling, degradation, or chemical erosion within weeks. This guide compares the three most common seat materials to help you make a data-driven decision for your application.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): The Cost-Effective All-Rounder
EPDM is the most widely used resilient material for butterfly valves, especially in water treatment and HVAC systems.
Performance: Excellent resistance to hot water, steam, and aging.
Temperature Range: -20°C to +120°C (-4°F to +248°F).
Compatible Media: Water, air, phosphate ester hydraulic fluids, and weak acids/alkalis.
The “Fatal” Weakness: Never use EPDM with oils. Exposure to mineral oils, lubricants, or hydrocarbons will cause EPDM to swell rapidly and fail completely.
Best Use Case: Municipal water, cooling loops, and fire protection systems.
2. Viton (FKM / Fluoroelastomer): The High-Heat & Oil Specialist
When your pipeline carries oil-based fluids or requires higher temperature resistance, Viton is the industry standard.
Performance: High chemical stability and heat resistance. It resists degradation from most hydrocarbons.
Temperature Range: -20°C to +200°C (-4°F to +392°F).
Compatible Media: Petroleum products, fuels, natural gas, strong oxidizers, and some concentrated acids.
The “Fatal” Weakness: Viton has poor resistance to low-molecular-weight organic acids (like acetic acid) and high-pressure steam. It is also 3 to 5 times more expensive than EPDM.
Best Use Case: Oil refineries, chemical processing, and gas pipelines.
3. PTFE (Teflon / Polytetrafluoroethylene): The Ultimate Corrosion Guard
For highly corrosive media where rubber fails, PTFE is the “Gold Standard.”
Performance: Nearly inert to almost all chemicals; features an extremely low coefficient of friction.
Temperature Range: -30°C to +180°C (-22°F to +356°F).
Compatible Media: Strong acids (Sulfuric/Nitric), strong alkalis, ultrapure water, and food-grade media.
The “Fatal” Weakness: Lack of Elasticity. PTFE is rigid. To achieve a tight seal, PTFE seats are usually “backed” by an elastic elastomer (like EPDM) to provide the necessary memory and resilience.
Best Use Case: Pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and Food & Beverage (FDA certified).
4. Selection Matrix: Quick Reference
| Feature | EPDM | Viton (FKM) | PTFE (Teflon) |
| Sealing Level | Class VI (Bubble-Tight) | Class VI (Bubble-Tight) | Class VI (with backup) |
| Oil Resistance | Poor | Excellent | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High | Superior (Inert) |
| Max Temperature | 120°C (248°F) | 200°C (392°F) | 180°C (356°F) |
| Friction/Torque | Moderate | Higher | Very Low |
| Relative Cost | Low ($) | High ($$$$) | Moderate-High ($$$) |
5. Engineer’s “Pro Tips” for Avoiding Failure
Q1: Why did my Viton seat fail in hot steam?
Expert Insight: This is a common mistake. While Viton is rated for 200°C, it degrades in the presence of high-pressure steam. For steam applications below 120°C, EPDM actually lasts much longer than Viton.
Q2: Is PTFE always better than rubber?
Expert Insight: Not necessarily. PTFE has “cold flow” characteristics, meaning it can permanently deform under high pressure or frequent cycling. Unless you have a chemical corrosion issue, a rubber seat (EPDM/Viton) generally offers a better “cycle life” due to its natural resilience.
Q3: What is “FDA-Grade” Sealing?
Expert Insight: For food or pharma, you must specify White PTFE or specific FDA-approved EPDM. Standard black rubber contains carbon black, which can leach into and contaminate sensitive media.
Conclusion: Engineering for the Environment
There is no “best” material, only the right material for the job.
Choose EPDM for general water systems to save cost.
Choose Viton for fuels and high-temperature oils to ensure safety.
Choose PTFE for aggressive chemicals or high-purity applications.