In modern hydraulic and pneumatic systems, the ability to control flow, pressure, and direction with surgical precision is the difference between a high-efficiency operation and a costly failure. While standard valves offer binary control, the proportional valve provides a bridge between simple switching and sophisticated servo-performance.

Table of Contents
Toggle1. What is a Proportional Valve? (Defining the Technology)
A proportional valve is a valve that relies on an external electronic controller to move its internal spool or poppet in proportion to an input signal (usually 0–10V or 4–20mA).
Unlike a standard solenoid valve, which is either fully open or fully closed, a proportional control valve can stop at any position in its stroke. This allows for infinitely variable control over the fluid’s speed, pressure, or flow rate.
2. Key Categories of Proportional Control Valves
To select the right solution, engineers must categorize valves based on their primary function. Our proportional valve lineup is divided into three core industrial categories:
A. Proportional Directional Control Valves
These valves manage both the direction of the fluid and the speed of the actuator. By varying the spool position, they control how much fluid reaches a cylinder or motor, allowing for smooth acceleration and deceleration.
B. Proportional Flow Control Valves
Ideal for applications requiring a constant speed despite fluctuating loads. The proportional flow valve adjusts its orifice size in real-time to maintain a precise flow rate.
C. Proportional Pressure Control Valves
These are used to regulate system pressure proportionally. They are essential in plastic injection molding, metal forming, and any process where “force control” is critical.
3. Proportional Valve vs. Standard Solenoid Valve: The 0-100% Advantage
Many maintenance teams ask: “Why should I invest in a proportional valve when I already have solenoid valves?” The answer lies in the linearity of control.
Solenoid Valve (Bang-Bang Control): Operates like a light switch. It is “On” or “Off.” This causes hydraulic shocks (water hammer), abrupt machine movements, and excessive wear on mechanical components.
Proportional Control Valve: Operates like a dimmer switch. It allows for a gradual increase from 0% to 100%. This proportional hydraulic valve control eliminates pressure spikes, improves machine lifespan, and allows for complex motion profiles that a standard valve simply cannot achieve.
4. The Role of the Proportional Valve Controller
A proportional hydraulic valve is only as smart as its brain. The proportional valve controller (or amplifier) takes the low-power signal from a PLC and converts it into the high-current PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal required to drive the valve’s solenoid.
Modern proportional hydraulic control valves often feature integrated electronics (OBE – On-Board Electronics), reducing wiring complexity and improving signal response time.
5. Understanding the Proportional Valve Symbol
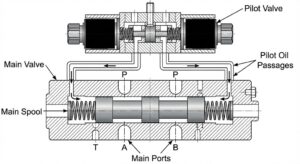
For engineers and designers, the proportional valve symbol is the primary language used in circuit diagrams. You can identify a proportional valve by the two horizontal lines added to the top and bottom of the standard valve envelope. These lines indicate that the valve is capable of “infinitely variable” positions.
6. Industrial Applications: From Water to Hydraulics
While often associated with oil, the demand for a proportional valve for water and pneumatic proportional valves is surging in automated cooling systems and precision gas mixing.
Hydraulic Systems: CNC machines, presses, and heavy lifting.
Water Treatment: Precision chemical dosing and flow stabilization.
Pneumatics: Tension control in paper mills and high-speed sorting.
Conclusion: Why Precision Matters
Choosing the right proportional control valve is about more than just moving a fluid; it is about optimizing your system for energy efficiency and mechanical longevity. By implementing hydraulic proportional valve control, facilities can reduce downtime by up to 30% and significantly improve product quality.