Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction: What Is Valve Trim?
Valve trim refers to all internal parts of a valve that come into direct contact with the fluid and control the flow. These components determine the valve’s performance, flow characteristics, sealing, and resistance to corrosion or erosion.
1.1 Valve Trim Definition
In valve engineering, valve trim includes the following parts:
Plug / Disc / Ball / Gate
Seat or seat ring
Stem
Backseat
Sleeve or guide bushings
Gaskets and packing (sometimes included depending on standard)
Trim = All wetted, functional, and replaceable parts controlling flow.
1.2 Why Valve Trim Matters
Valve trim determines:
Flow control accuracy
Shutoff capability
Chemical compatibility
Resistance to erosion, corrosion, cavitation
Safety performance
Valve lifespan
Trim selection is critical for:
Oil & gas
Chemical & petrochemical
Refining
Power generation
Water and wastewater
Marine and offshore
2. What Components Are Included in Valve Trim?
(Full technical explanation)
2.1 Gate Valve Trim
Includes:
Wedge / gate
Seats
Stem
Backseat bushing
Seat ring
2.2 Globe Valve Trim
Disc (plug)
Seat ring
Stem
Cage (control valve)
2.3 Ball Valve Trim
Ball
Seats (soft or metal)
Stem
2.4 Control Valve Trim
The most complex:
Plug
Seat
Stem
Cage
Guides
Seals
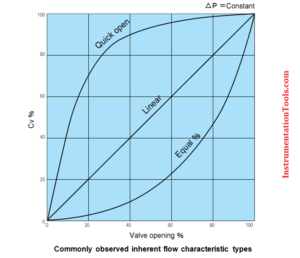
Characterization elements (equal %, linear)
Includes Cavitation-resistant trims:
Multi-hole cage trim
Multi-stage trim
Anti-cavitation trim
Noise-reduction trim
3. Valve Trim Material Overview
Valve trim uses different material classes:
3.1 Stainless Steels (Trim 8, Trim 5, etc.)
304
316
316 + HF
Stellite hardfacing
3.2 Carbon Steels
A105
410 SS faced
HF coatings
3.3 Hardfacing Alloys
Used for severe service:
Stellite 6
Alloy 6
Tungsten carbide
Colmonoy
Chromium carbide
3.4 Special Alloys
Monel
Inconel
Hastelloy
Duplex / Super Duplex
Titanium
3.5 Soft Trim Materials (control valves)
PTFE
RPTFE
EPDM
Viton
PEEK
Delrin
4. API Valve Trim Chart (FULL)
✔ Covers API 600, 602, 603, 608
✔ Includes Trim Numbers 1–16
✔ Includes materials & applications
✔ High-value SEO section
# 5. Full API Valve Trim Chart (API 600, API 602, API 603, API 608)
The most complete API valve trim chart available online.
This chart lists all commonly used API valve trim numbers, materials, and recommended applications.
5.1 API Trim Chart (Master Table)
✔ Covers Trim Numbers 1–16
✔ Includes Material, Hardfacing, Seat Type, and Applications
✔ Ideal for SEO & Engineering Reference
API Valve Trim Chart (Full Table)
| Trim No. | Stem / Disc / Gate Material | Seat / Seat Ring Material | Hardfacing / Overlay | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trim 1 | 410 SS | 410 SS | None | Clean water, steam, general service |
| Trim 2 | 304 SS | 304 SS | None | Corrosion-resistant services |
| Trim 3 | 304 SS | 410 SS | None | Mixed services, moderate corrosion |
| Trim 4 | 410 SS | 304 SS | None | Corrosive water, mild chemicals |
| Trim 5 | 410 SS | 410 SS HF | Stellite (CoCr alloy) | Erosion, high temp, steam (MOST COMMON HARD TRIM) |
| Trim 6 | 410 SS | 410 SS | 410 + HF on seating | Upgraded wear resistance |
| Trim 7 | 410 SS | 316 SS | None | Chlorides, moderate corrosion |
| Trim 8 | 316 SS | 316 SS | None | Chemical service (MOST COMMON SS TRIM) |
| Trim 9 | Monel | Monel | None | Sea water, H₂S, sour gas |
| Trim 10 | 316 SS | 316 SS HF | Stellite overlay | Severe corrosion + high temp |
| Trim 11 | Alloy 20 | Alloy 20 | None | Sulfuric acid environments |
| Trim 12 | 316 SS | 316 SS | Stellite seat + hardfaced disc | High cycle, high temp |
| Trim 13 | 316 SS | 316 SS | Stellite both sides | Severe service + erosion |
| Trim 14 | Hastelloy | Hastelloy | None | Strong acids, chlorides |
| Trim 15 | Titanium | Titanium | None | Seawater, brine, high chlorides |
| Trim 16 | Duplex SS | Duplex/Super Duplex | None | Offshore, sour service, high chloride |
5.2 API Trim Quick Summary (Easy Reference)
Most Common API Trims
Trim 1 → Basic service
Trim 5 → Steam, high temp, erosion
Trim 8 → Chemical service
Trim 12 / 13 → Severe service, high erosion
Trim 16 → Offshore & high chlorides
Corrosion-resistant Trims
Trim 8 (316 SS)
Trim 9 (Monel)
Trim 14 (Hastelloy)
Trim 15 (Titanium)
Hardfaced Trims
Trim 5
Trim 10
Trim 12
Trim 13
These are used when erosion or high temperatures are expected.
# 6. Trim 5 vs Trim 8 (Important Comparison Section)
| Feature | Trim 5 | Trim 8 |
|---|---|---|
| Material | 410 SS + Stellite | 316 SS |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Temperature Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Erosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Steam Service | ✔ Recommended | ✘ Not recommended |
| Chemical Service | ✘ Limited | ✔ Recommended |
| Typical Use | Steam, gas, high temp | Water treatment, chemicals |
Which one should you choose?
High temperature, steam, erosion → Trim 5
Chemical service, chlorides, acidic environments → Trim 8
# 7. API 600 / API 602 Trim Chart (Simplified)
API 600 (Gate / Globe / Check Valves)
Most used trims:
| API 600 Trim | Description |
|---|---|
| Trim 1 | 410 SS basic service |
| Trim 5 | 410 SS + Stellite seat (high temp) |
| Trim 8 | 316 SS (chemical) |
| Trim 12 | 316 SS + HF seat (high pressure/high temp) |
| Trim 16 | Duplex/Super Duplex |
API 602 (Small Forged Steel Valves)
Common trims:
| API 602 Trim | Description |
|---|---|
| Trim 1 | 410 SS |
| Trim 5 | Stellite faced |
| Trim 8 | 316 SS |
| Trim 9 | Monel for sour service |
| Trim 16 | Duplex |
# 8. NACE Valve Trim Chart (MR0175 / ISO 15156)
NACE-Compliant Trims
Used for sour gas (H₂S) applications.
| Trim No. | NACE? | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Trim 1 (410 SS) | ❌ No (unless special treatment) | Can suffer SSC |
| Trim 8 (316 SS) | ✔ Yes | Very common |
| Trim 9 (Monel) | ✔ Yes | Excellent sour service |
| Trim 14 (Hastelloy) | ✔ Yes | Severe H₂S, chlorides |
| Trim 16 (Duplex) | ✔ Yes | High strength + chloride resistance |
Most used NACE trim:
→ Trim 8 (316 SS) and Trim 9 (Monel)
# 9. Valve Trim Types (Full Classification)
This section covers the keyword cluster:
valve trim types
control valve trim
valve trim material types
9.1 By Material
Carbon steel trims
Stainless steel trims
Alloy trims
Hardfaced trims
Soft seat trims
Elastomer trims
9.2 By Service Type
Standard trim
Corrosion-resistant trim
Erosion-resistant trim
High-temperature trim
Cryogenic trim
NACE sour gas trim
9.3 In Control Valves
Cage-guided trim
Multi-stage trim (anti-cavitation)
Noise-reducing trim
Quick-change trim
Characterized trim (equal %, linear, modified linear)
10. Valve Trim Material Selection Guide (How to Choose the Right Trim)
Selecting the correct valve trim material determines whether a valve lasts 30 years or fails in 3 months. The wrong trim leads to leakage, galling, corrosion, erosion, or complete failure.
Below is a step-by-step material selection guide used by engineers.
Step 1 — Define the Fluid Type
Material compatibility is the first filter.
✔ Compatible With Most Fluids
304, 316 stainless steel
Monel
Hastelloy B/C
Bronze
✔ For Corrosive / Chloride / Sour Service
316 SS
316+Hardfacing
Duplex / Super Duplex
Hastelloy C276
Monel 400
Inconel 625
✔ For Hydrocarbon / Steam
410 SS (hardened)
13Cr
Stellite hardfacing
Step 2 — Identify Temperature Range
| Temperature | Recommended Trim Materials |
|---|---|
| -20°C to 200°C | 304, 316 SS, Bronze |
| 200°C–400°C | 410 SS, 13Cr, Stellite |
| 400°C–600°C | Stellite, Inconel |
| > 600°C | Inconel 718, Stellite |
Step 3 — Consider Pressure & Velocity (Erosion Risk)
High velocity or flashing → erosion-resistant trim.
Best choices:
Stellite 6
Tungsten carbide
410 SS hardened
Inconel / Monel
Avoid bronze or soft stainless steels in erosive media.
Step 4 — Check Need for Hardfacing / Anti-Galling
Galling often occurs in stainless-on-stainless trim.
Use:
Stellite facing
Nitrided surfaces
Hardened 410 SS
Step 5 — Sour Service (H₂S) Requirements – NACE MR0175 Compatibility
✔ Monel
✔ Inconel
✔ Hastelloy
✔ Duplex / Super Duplex
✔ Stellite
✘ 410 SS (only limited use unless specially heat treated)
✘ 13Cr (risk of SSC)
For sour applications, always verify:
Hardness limits
SSC resistance
Sulfide cracking compliance
11. Valve Trim Types (Based on Function)
A. Control Valve Trim Types
Cage-guided trim – stable, low vibration
Plug & seat trim – common for throttling
Multi-hole / Anti-cavitation trim – eliminates noise and flashing
Equal percentage / linear trim – flow characteristic options
B. On–Off Valve Trim Types
Wedge gate trim
Globe plug trim
Ball valve seats & ball trims
Butterfly valve discs
12. API Trim 1–17 Explained (Material Overview)
You have the full chart earlier—this section gives real-world use cases.
Trim 1 – 410 SS
Best for:
Water
Steam
General hydrocarbons
Moderate temp applications
Avoid:
Chlorides (pitting)
Sour service
Trim 5 – 410 SS + Stellite
Best for:
High-temperature valves
Steam service
Anti-galling, high wear applications
Common in:
Refinery isolation valves
Power plants
High-cycle globe valves
Trim 8 – 316 SS
Best for:
Corrosive fluids
Chemical plants
Moderate chlorides
Avoid:
High-cycle erosion
Cavitation
Trim 10 – Monel 400
Best for:
Brine
Saltwater
Sour gas
Excellent chloride resistance.
Trim 12 – 316 SS + Hardfacing
Best for:
Corrosive + erosive service
Offshore
Chemical injection lines
Trim 13 – Alloy 20
Best for:
Sulfuric acid
Highly acidic service
Severe corrosion environments
Trim 16 – Hastelloy C
Best for:
Corrosive + high temp
Chlorine, seawater
Chemical reactors
Trim 17 – Stellite
Best for:
Extreme erosion
High temperature
Severe throttling
Cavitation control
Most durable trim material.
13. Valve Trim Number System (How to Read It)
The “trim number” defines:
Stem material
Plug/disc material
Seat material
Hardfacing type
Facing material
This ensures standardization across manufacturers:
API 600 (gate valves)
API 602 (compact gates/globes)
API 603 (corrosion-resistant valves)
Important: Trim number ≠ body material.
Trim only refers to internal wetted moving parts.
14. Control Valve Trim (Special Features)
Control valve trim includes:
Seat ring
Plug
Stem
Guide bushings
Cage (optional)
Anti-cavitation elements
Different control trim designs:
Single-stage
Multi-stage
Multi-hole cage
Low-noise trim
Anti-flashing trim
15. Gate Valve Trim Chart (API 600 Focus)
Common gate valve trim selections:
| API Trim | Gate Valve Application |
|---|---|
| Trim 1 | Water, steam |
| Trim 5 | Steam, refinery |
| Trim 8 | Corrosive chemicals |
| Trim 10 | Seawater, sour service |
| Trim 12 | Corrosive + erosive fluids |
16. Valve Body Material vs Valve Trim (Don’t Confuse Them)
Valve body material = main pressure boundary
Trim material = internal sealing & moving parts
Common combination examples:
| Body Material | Typical Trim |
|---|---|
| WCB | Trim 1, 5 |
| CF8M | Trim 8, 12 |
| Duplex | Trim 12, 16 |
| Bronze | Trim 1, 8 |
17. FAQs
1. What is valve trim?
All internal wetted parts that control, shut off, or regulate flow.
2. Does body material determine trim?
No — trim is chosen based on fluid, temperature, and pressure.
3. Is Stellite the best trim?
Yes for:
High temp
Severe erosion
High cycle service
But not needed for simple water or low-pressure service.
4. What is the difference between Trim 5 and Trim 8?
Trim 5 = 410 SS + Stellite (strong, good for steam)
Trim 8 = 316 SS (corrosion resistance)
5. What trim is best for seawater?
Monel (Trim 10)
or
Duplex + Stellite (Custom trims)