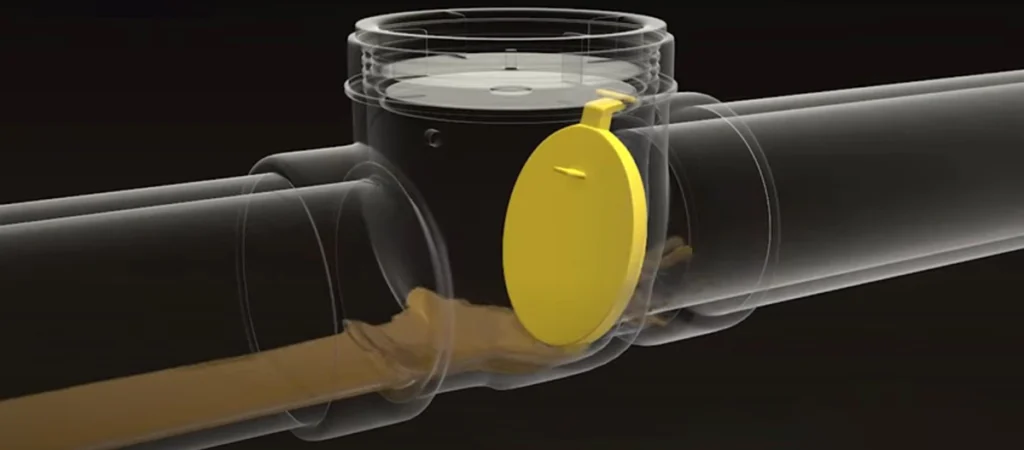
A backwater valve—also known as a backflow prevention valve or sewer backflow valve—is a plumbing device installed in the building’s drainage system to prevent sewage from flowing backward into the house. It acts as a one-way gate: wastewater can exit your property, but contaminated water from the municipal sewer line cannot return during flooding, blockages, or heavy rain.
Backwater valves are essential in homes and commercial buildings located in areas prone to sewer surcharges or high rainfall.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow a Backwater Valve Works
A backwater valve contains an internal flap or gate that opens when water flows outward from the building. If sewage begins to reverse direction, the flap closes automatically, forming a tight seal to stop dirty water from entering.
Flow direction:
✔ Outflow → valve opens
✘ Backflow → valve closes
Some models include a transparent lid, allowing quick inspection to see if the flap is functioning or blocked.
Why Backwater Valves Are Important
1. Prevent Sewer Flooding and Property Damage
Sewage backup can destroy floors, appliances, and furniture, and create dangerous health hazards. A backwater valve is one of the most effective protections.
2. Required by Building Codes
Many cities require backwater valves in basements or low-level plumbing fixtures connected to municipal sewer lines.
3. Low Maintenance, High Protection
With simple annual cleaning, backwater valves offer long-term safety.
Common Types of Backwater Valves
1. Flapper Backwater Valve
Uses a swing flap
Suitable for residential wastewater
Easy to inspect and maintain
2. Gate/Knife Backwater Valve
Heavy-duty design
Offers a stronger, more secure seal
Used in municipal or industrial systems
3. Ball-Type Backwater Valve
Uses a rubber-coated ball to block reverse flow
Excellent for sewage with suspended solids
4. Combination Backwater Valve
Includes built-in cleanouts for inspection and clog removal
Where Backwater Valves Are Installed
Typically installed in the building’s main sewer line, especially in:
Basements
Crawl spaces
Low-lying drainage areas
Areas below street sewer level
Homes in flood-prone regions often place a backwater valve just upstream of the property line for maximum protection.
Signs You Need a Backwater Valve
You should consider adding a backwater valve if you experience:
Sewage smell from floor drains
Gurgling sounds in toilets or sinks
Previous sewer backup incidents
Neighborhood sewer overload during storms
Maintenance Tips
To ensure proper operation:
Inspect every 6–12 months
Remove debris, grease, or wipes caught at the flap
Ensure the flap moves freely
Check seals for cracks or aging
Backwater Valve vs. Check Valve
Although similar, they are not the same:
| Feature | Backwater Valve | Check Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Household sewer lines | Water or industrial pipelines |
| Design | Prevents sewer backup | Prevents flow reversal |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic cleaning | Minimal maintenance |
| Flow Media | Sewage and solids | Water, gas, clean fluids |
Conclusion
A backwater valve is a critical device for preventing sewer backup and protecting your home from flooding damage. Simple, reliable, and inexpensive, it ensures wastewater flows out but never returns. Whether you are a homeowner seeking protection or a contractor designing a drainage system, installing a backwater valve is an essential safety measure.