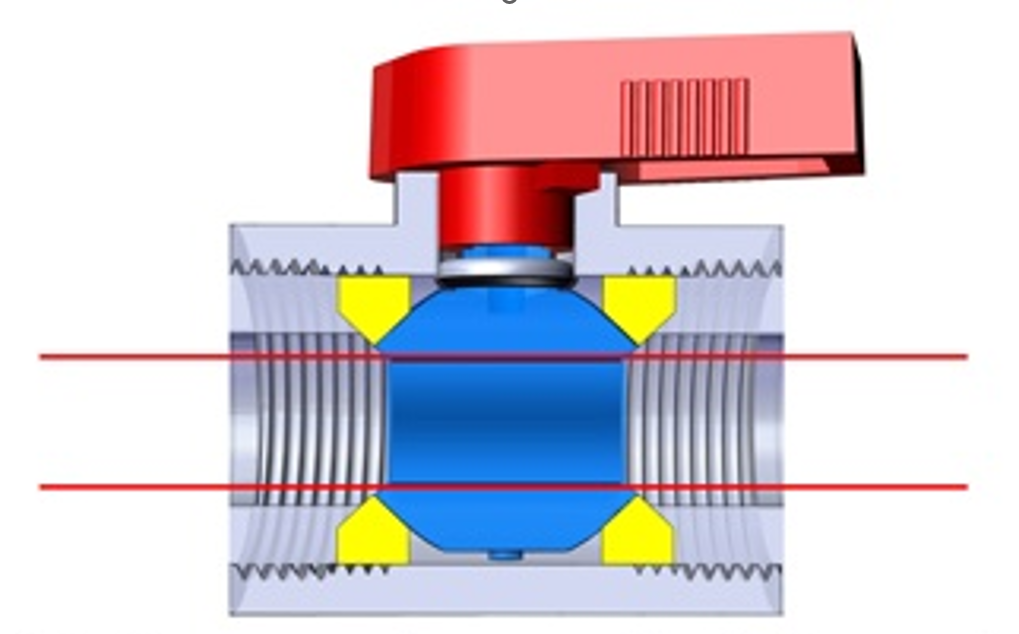
A full port ball valve (also called a full bore ball valve) is a type of quarter-turn valve designed to provide unrestricted flow through a pipeline. Unlike reduced-port valves, a full port ball valve has an internal bore that matches the inside diameter of the pipe, allowing fluid to pass through with minimal pressure drop.
Understanding what a full port ball valve is—and when to use one—can help prevent flow restrictions, reduce energy loss, and extend the life of pumps and piping systems.
Table of Contents
ToggleQuick Definition
What is a full port ball valve?
A full port ball valve is a ball valve whose internal opening (bore) is the same size as the pipe’s inner diameter, allowing straight-through, full-flow operation.
How a Full Port Ball Valve Works
A full port ball valve operates using a hollow, perforated ball that rotates 90 degrees.
Open position:
The bore aligns perfectly with the pipe, allowing full flow.Closed position:
The solid side of the ball blocks the flow completely.
Because the bore is full size, fluid experiences no significant restriction or turbulence as it moves through the valve.
Full Port vs Reduced Port Ball Valve
Comparison Table
| Feature | Full Port Ball Valve | Reduced Port Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Bore Size | Same as pipe ID | Smaller than pipe ID |
| Flow Restriction | None | Moderate |
| Pressure Drop | Minimal | Higher |
| Flow Efficiency | Very high | Lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Use | High-flow, critical systems | General shut-off |
Why Choose a Full Port Ball Valve?
1. Maximum Flow Capacity
Because there is no internal restriction, full port ball valves maintain the system’s original flow rate.
2. Minimal Pressure Drop
Ideal for systems where pressure loss can reduce performance, such as pump-driven applications.
3. Reduced Turbulence
Less turbulence means:
Lower risk of erosion
Reduced noise
Longer valve and pipe life
4. Pigging Capability
Full port ball valves allow pipeline cleaning pigs to pass through, making them essential in oil, gas, and chemical pipelines.
Common Applications of Full Port Ball Valves
Full port ball valves are widely used in systems that demand high efficiency and reliability, including:
Oil & gas pipelines
Chemical processing plants
Water treatment facilities
Industrial pumping systems
HVAC systems
Fire protection systems
Irrigation mainlines
Food & beverage processing
Full Port vs Standard Port vs V-Port Ball Valves
| Valve Type | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|
| Full Port | Maximum flow, minimal pressure loss |
| Standard (Reduced) Port | Cost-effective shut-off |
| V-Port | Flow modulation and control |
If your system requires on/off isolation with no flow loss, full port is the best choice.
When Is a Full Port Ball Valve Necessary?
You should use a full port ball valve when:
Flow rate must remain unchanged
Pressure drop must be minimized
Pumps are sensitive to restriction
Pipeline pigging is required
High-viscosity fluids are used
Solids or slurries pass through the valve
When a Full Port Ball Valve May Be Overkill
A full port ball valve may not be necessary if:
The valve is used only for isolation
Flow rate is not critical
Budget constraints exist
Space is limited
In these cases, a reduced port ball valve may be sufficient.
Materials Available for Full Port Ball Valves
Full port ball valves are available in a wide range of materials:
Brass – Plumbing and potable water
Stainless Steel – Corrosive and high-temperature environments
Carbon Steel – Oil & gas applications
PVC / CPVC – Irrigation and chemical handling
Full Port Ball Valve Advantages & Disadvantages
Pros
✔ Full, unrestricted flow
✔ Low pressure loss
✔ High durability
✔ Excellent sealing
✔ Suitable for pigging
Cons
✘ Higher cost
✘ Larger size and weight
✘ Not ideal for throttling flow
FAQ
Is a full port ball valve better than a standard port?
It depends on the application.
Full port valves are better for high-flow systems, while standard port valves are sufficient for basic shut-off needs.
Does a full port ball valve increase flow?
It does not increase flow beyond pipe capacity—but it prevents flow reduction caused by internal restrictions.
Can a full port ball valve be used for throttling?
No. Ball valves are designed for on/off service, not flow regulation.
Are full port and full bore ball valves the same?
Yes. “Full port” and “full bore” refer to the same valve design.
Conclusion
A full port ball valve is the ideal choice when flow efficiency, pressure stability, and system performance matter. While it costs more than a reduced-port valve, the benefits often outweigh the price in critical systems.
If your application demands unrestricted flow and long-term reliability, a full port ball valve is the right solution.