Preventing backflow is essential in plumbing, irrigation, and fuel systems. One of the simplest and most effective tools for this purpose is the anti-siphon valve. Whether you’re dealing with contaminated irrigation water, residential hose bibs, or marine fuel tanks, anti-siphon protection plays a critical role in ensuring safety and system integrity.
This comprehensive guide explains what an anti-siphon valve is, how it works, why it matters, and where it is used across different industries.
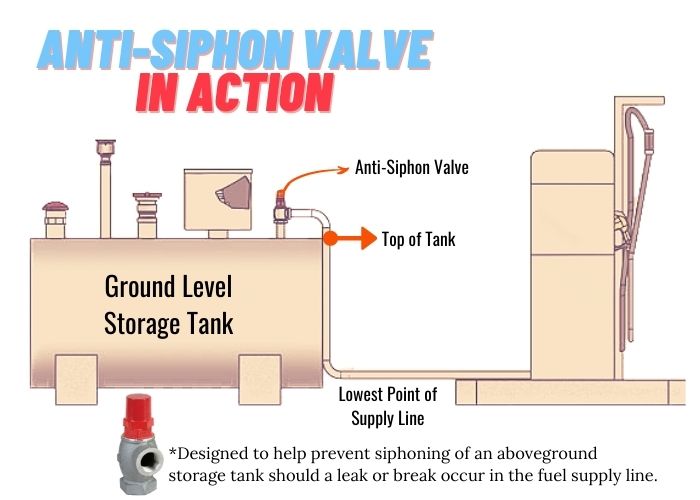
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is an Anti-Siphon Valve?
Anti-Siphon Meaning and Basic Definition
An anti-siphon valve is a device designed to prevent siphoning, which is the unwanted reversal of fluid flow caused by pressure differences.
Siphoning occurs when:
The outlet is lower than the inlet
Pressure drops suddenly
A vacuum is created
Fluid begins to flow backward
The term “anti-siphon” simply means:
➡️ A device that prevents reverse flow.
Without anti-siphon protection, contaminated water or fuel can be pulled back into clean supply lines, causing pollution, safety hazards, or equipment failures.
Why Anti-Siphon Protection Is Necessary
1. Preventing Contamination in Plumbing Systems
If a hose or pipe becomes submerged in dirty water, pressure loss can cause that water to siphon back into your home’s potable water supply.
Anti-siphon valves break the vacuum before contamination enters the system.
2. Protecting Irrigation Systems
Irrigation lines often contact:
Soil
Fertilizers
Pesticides
Standing water
Without anti-siphon devices, these substances can flow back into household plumbing.
3. Preventing Fuel Theft and Fuel Leakage
In automotive, generator, and marine fuel tanks, siphoning can cause:
Fuel theft
Fuel spills
Fire hazards
Fuel anti-siphon valves stop reverse flow, protecting the fuel system.
4. Meeting Building Codes and Regulations
Many regions require anti-siphon devices on:
Hose bibs
Sprinkler systems
Outdoor faucets
Fuel systems on boats
Compliance is both a safety and legal requirement.
How Anti-Siphon Valves Work
The Physics of Siphoning
Siphoning occurs due to a pressure differential. When pressure on the downstream side drops below the upstream side, fluid is forced backward — unless a mechanism blocks it.
An anti-siphon valve prevents this by:
✔ Introducing air into the system when vacuum forms
✔ Breaking the siphon
✔ Stopping reverse flow instantly
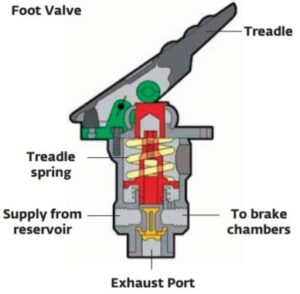
Core Components of Anti-Siphon Valves
Most anti-siphon valves include:
Air inlet / vacuum breaker (admits air when pressure drops)
Spring-loaded mechanism (keeps flow one-directional)
Check valve (often used in fuel applications)
Diaphragm (in irrigation valves)
Outlet and inlet ports
Types of Anti-Siphon Devices
1. Atmospheric Vacuum Breaker (AVB)
Uses gravity and air openings to prevent backflow.
2. Pressure Vacuum Breaker (PVB)
Stronger, used in pressurized irrigation systems.
3. Mechanical Anti-Siphon Valve
Used in sprinkler systems, often combined with a solenoid.
4. Fuel Tank Anti-Siphon Valve
Prevents fuel theft and reverse fuel flow.
5. Anti-Siphon Hose Bib
Outdoor faucet with a built-in vacuum breaker.
Applications of Anti-Siphon Valves
1. Irrigation Systems
Sprinkler systems must include anti-siphon protection to prevent dirt, fertilizer, and wastewater from entering drinking water lines.
2. Garden Hose and Hose Bibs
Outdoor faucets often have built-in or add-on vacuum breakers to stop backflow from contaminated hoses.
3. Residential Plumbing
Anywhere water might flow backward (bathtubs, exterior faucets, etc.), anti-siphon devices are required.
4. Marine and Automotive Fuel Tanks
Fuel systems use anti-siphon valves to:
Prevent theft
Stop fuel leakage
Prevent fires
Meet Coast Guard regulations
5. Industrial Systems
Factories use anti-siphon protection for chemical lines, waste systems, and fluid transfer equipment.
Benefits of Anti-Siphon Valves
1. Prevents Contamination
Stops dirty water from flowing back into clean supply lines.
2. Protects Equipment and Systems
Prevents reverse flow damage in pumps, engines, and plumbing.
3. Enhances Safety
Stops fuel leakage, protects drinking water, and ensures code compliance.
4. Required by Code
Most plumbing and irrigation codes require anti-siphon devices — making them essential.
Signs You Need an Anti-Siphon Valve
You may need to add or replace an anti-siphon valve if you experience:
Discolored water
Strange smells from hoses or faucets
Fuel siphoning incidents
Loss of water pressure
Dripping or leaking from hose bibs
These symptoms indicate backflow or vacuum issues.
Conclusion
An anti-siphon valve is a critical safety device used to prevent reverse fluid flow in plumbing, irrigation, and fuel systems. By breaking a vacuum and blocking siphon action, it protects clean water supplies, prevents fuel theft, and ensures system safety.
Whether you’re maintaining an irrigation system, installing a hose bib, or securing a fuel tank, anti-siphon valves are essential components that play a key role in system reliability and regulatory compliance.