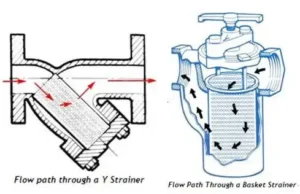
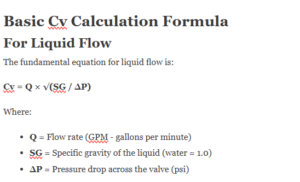
In the global energy industry, the American Petroleum Institute (API) provides the “gold standard” for equipment safety and performance. For valve manufacturers and engineers, following API standards is not just about quality—it is the mandatory “passport” to enter the oil, gas, and petrochemical markets.

Whether you are looking for API petroleum standards for a refinery project or trying to understand the API standard list for procurement, this guide breaks down the most critical technical specifications.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. What is the American Petroleum Institute (API)?
The American Petroleum Institute (API), founded in 1919, is the primary organization for the U.S. oil and natural gas industry. It is globally recognized for developing technical API guidelines and codes that ensure operational safety, environmental protection, and equipment reliability.
For the valve industry, API standards govern everything from the thickness of the valve wall to the specific metal alloys used in high-pressure environments.
2. Core API Valve Standards: A Quick Reference List
If you are involved in the design or procurement of valves, you must be familiar with these key American Petroleum Institute codes:
A. API 6D: Specification for Pipeline Valves
This is the “Bible” for the oil and gas midstream sector. It covers ball, check, gate, and plug valves used in long-distance pipelines.
Key Focus: Pressure ratings, dimensions, and rigorous testing for high-pressure transport.
B. API 600: Steel Gate Valves (Bolted Bonnet)
The most common standard for heavy-duty refinery service. API 600 gate valves are known for their “thick walls” and superior durability.
Key Focus: Minimum wall thickness and stuffing box dimensions for maximum safety.
C. API 602: Small Forged Steel Valves
Covers compact gate, globe, and check valves (DN100 and smaller). These are the workhorses of chemical plants and high-pressure steam lines.
D. API 608: Metal Ball Valves
The standard for flanged, threaded, and welding end ball valves. It ensures that ball valves can handle the mechanical stress of oil and gas processing.
E. API 598: Valve Inspection and Testing
This is the universal testing standard. Almost all API petroleum valves must pass API 598 tests before they leave the factory.
Requirements: High-pressure shell tests and low-pressure seat leakage tests.
3. Specialized Standards: Fire-Safety & Fugitive Emissions
As global safety and environmental (ESG) regulations tighten, two specific API standards have become industry benchmarks:
API 607 / API 6FA: Fire Test Standards. These ensure that even if a refinery fire occurs, the valve will maintain a basic seal to prevent feeding the flames.
API 622 / API 641: Fugitive Emission Testing. These focus on reducing the leakage of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to protect the atmosphere. (Crucial for NFPA – National Fire Protection Association compliance).
4. Comparison Table: Choosing the Right API Standard
| Standard | Valve Type | Primary Application |
| API 6A | Wellhead Equipment | Upstream Drilling & Oil Trees |
| API 6D | Pipeline Valves | Midstream Transportation |
| API 600 | Cast Steel Gate Valves | Downstream Refineries |
| API 609 | Butterfly Valves | Water & Chemical Processing |
| API 594 | Check Valves | Backflow Prevention |
5. Why API Monogrammed Valves Matter
Why do customers pay a premium for API petroleum standards?
Safety: API-certified valves have higher wall thicknesses and stricter material requirements than general industrial valves.
Global Tender Access: Most international oil companies (like Aramco, Shell, or ExxonMobil) require an API 6D or 600 monogram as a mandatory bidding condition.
Traceability: API requires full material traceability and documented testing for every valve produced.
Conclusion: The “Gold Standard” for Reliability
Understanding the American Petroleum Institute guidelines is the first step toward building a safe and efficient fluid control system. At TOT Valve, we specialize in manufacturing valves that meet and exceed these rigorous API standards.