A solenoid valve is an electromechanically operated valve that uses an electromagnetic coil (solenoid) to control the flow of liquids or gases. When electrical current passes through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that moves a plunger to open or close the valve—allowing precise, remote, and automated control of fluid flow.
Solenoid valves are found everywhere: in washing machines, irrigation systems, cars, industrial automation, medical equipment, and countless other applications. In this guide, we’ll explain how solenoid valves work, explore the different types, and help you understand which one is right for your application.
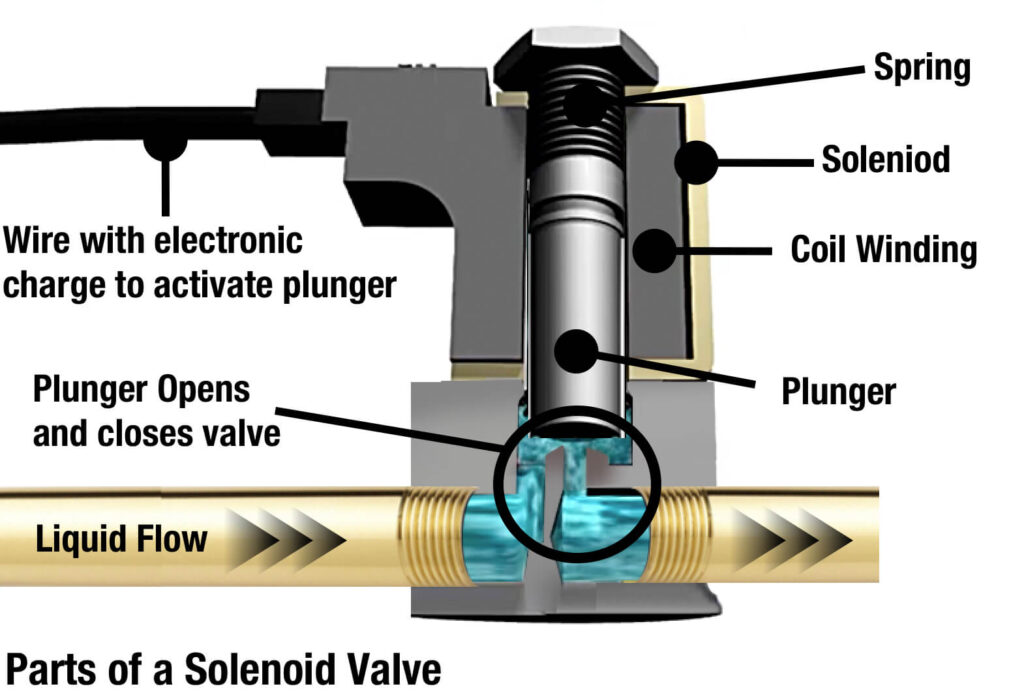
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is a Solenoid?
Before diving into solenoid valves, let’s understand the core component: what is a solenoid?
A solenoid is an electromagnetic device consisting of a wire coil wrapped around a movable metal core (plunger). When electricity flows through the coil:
- It generates a magnetic field
- The magnetic field pulls or pushes the metal plunger
- This linear motion can be used to perform mechanical work
In a solenoid valve, this electromagnetic action opens or closes a valve port, controlling fluid flow without any manual intervention.
How Does a Solenoid Valve Work?
The working of solenoid valve is based on electromagnetic principles combined with fluid dynamics.
Basic Operation
When de-energized (no power):
- The plunger is held in position by a spring
- Depending on valve type, the port is either open or closed
When energized (power applied):
- Electric current flows through the coil
- Magnetic field is generated
- Plunger moves against the spring force
- Valve port opens or closes (opposite of de-energized state)
When power is removed:
- Magnetic field collapses
- Spring returns plunger to original position
- Valve returns to its default state
Solenoid Valve Working Principle
The solenoid valve working principle varies slightly depending on the operating mechanism:
| Type | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Direct acting | Plunger directly opens/closes the orifice | Low flow, low pressure |
| Pilot operated | Small pilot valve controls larger main valve using system pressure | High flow, high pressure |
| Semi-direct | Combines direct action with pressure assistance | Medium flow, variable pressure |
Solenoid Valve Diagram
Understanding solenoid valve components helps with selection and troubleshooting.
Basic Solenoid Valve Schematic Diagram
┌─────────────────┐
│ Coil Housing │
│ ┌───────────┐ │
────►│ │ Solenoid │ │◄──── Electrical
Power │ │ Coil │ │ Connection
│ └─────┬─────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌────▼────┐ │
│ │ Plunger │ │
│ └────┬────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ┌────▼────┐ │
│ │ Spring │ │
└───┴────┬────┴───┘
│
══════════════╪══════════════
Inlet │ Outlet
Port Orifice Port
══════════════════════════════
Valve Body
Key Components
- Solenoid coil: Generates magnetic field when energized
- Plunger/armature: Moves in response to magnetic field
- Spring: Returns plunger when power is removed
- Orifice: Opening through which fluid flows
- Valve body: Houses ports and flow paths
- Seals: Prevent leakage between components
Types of Solenoid Valves
Different applications require different types of solenoid valves. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown:
By Port Configuration
2-Way Solenoid Valve
- Ports: 1 inlet, 1 outlet
- Function: Simply opens or closes flow
- Uses: On/off control, isolation
3-Way Solenoid Valve
- Ports: 1 inlet, 1 outlet, 1 exhaust
- Function: Directs flow between two paths
- Uses: Single-acting cylinders, diverting flow
4-Way Solenoid Valve
- Ports: 1 pressure, 2 cylinder, 1 exhaust
- Function: Controls double-acting cylinders
- Uses: Pneumatic and hydraulic actuators
5-Way Solenoid Valve
- Ports: 1 pressure, 2 cylinder, 2 exhaust
- Function: Independent exhaust control
- Uses: Advanced pneumatic control, speed regulation
By Default State
| Type | De-energized State | Energized State | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normally Closed (NC) | Closed | Open | Safety applications—fails closed |
| Normally Open (NO) | Open | Closed | Cooling systems—fails open |
| Universal | Configurable | Configurable | Flexible installations |
By Operating Mechanism
Direct Acting Solenoid Valve
- Plunger directly opens/closes orifice
- Works at zero pressure differential
- Best for: Low flow rates, vacuum applications
- Orifice size: Typically small
Pilot Operated (Indirect) Solenoid Valve
- Uses system pressure to operate main valve
- Requires minimum pressure differential to function
- Best for: High flow rates, large pipe sizes
- More energy efficient for large valves
Semi-Direct Acting Solenoid Valve
- Combines direct and pilot operation
- Works from zero pressure to high pressure
- Best for: Applications with variable pressure conditions
Solenoid Valve Types Comparison
| Feature | Direct Acting | Pilot Operated | Semi-Direct |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum pressure | 0 bar | 0.3-0.5 bar typical | 0 bar |
| Flow capacity | Low-Medium | High | Medium-High |
| Response time | Fast | Slower | Medium |
| Power consumption | Higher for large valves | Lower | Medium |
| Cost | Lower for small sizes | Lower for large sizes | Higher |
| Complexity | Simple | More complex | Moderate |
What Is a Solenoid Valve Used For?
The purpose of a solenoid valve is to provide fast, reliable, automated control of fluid flow. Here are the most common applications:
Industrial Automation
- Pneumatic cylinder control
- Process control systems
- Packaging machinery
- Conveyor systems
- Automated assembly lines
HVAC and Refrigeration
- Refrigerant flow control
- Hot water circulation
- Steam control
- Zone heating/cooling
Water and Irrigation
- Automatic sprinkler systems
- Washing machines and dishwashers
- Water treatment systems
- Fountain and pool controls
Automotive Applications
What is a solenoid valve in a car? Vehicles use numerous solenoid valves for:
- Fuel injection systems
- Transmission fluid control
- Emission control (EGR valves)
- Turbocharger boost control
- ABS brake systems
- HVAC blend door control
Medical and Laboratory
- IV fluid control
- Dialysis machines
- Analytical instruments
- Dental equipment
- Oxygen delivery systems
Food and Beverage
- Beverage dispensing
- Coffee machines
- Steam and water control
- Clean-in-place (CIP) systems
Pneumatic Systems
Solenoid valves are essential in pneumatic systems where they control air flow to:
- Actuate cylinders
- Operate air tools
- Control pneumatic grippers
- Sequence automated operations
Solenoid Valve Specifications
When selecting a solenoid valve, consider these key specifications:
Electrical Specifications
| Parameter | Common Options | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 12V DC, 24V DC, 24V AC, 110V AC, 220V AC | Match to control system |
| Power consumption | 2W to 30W+ | Affects heat generation and efficiency |
| Duty cycle | Continuous (100%) or intermittent | Continuous for always-on applications |
| Protection class | IP65, IP67, IP68 | Higher for wet/dusty environments |
Fluid Specifications
| Parameter | What to Consider |
|---|---|
| Media | Water, air, oil, steam, corrosive fluids |
| Temperature | Operating range of seals and body materials |
| Pressure | Maximum operating pressure and pressure differential |
| Viscosity | High viscosity may require larger orifice |
Physical Specifications
- Port size: 1/8″ to 3″ or larger
- Connection type: NPT, BSP, flanged, push-fit
- Body material: Brass, stainless steel, plastic, aluminum
- Seal material: NBR, EPDM, FKM (Viton), PTFE
How to Select the Right Solenoid Valve
Step 1: Define Your Application
- What fluid will flow through? (Air, water, oil, chemicals)
- What is the flow rate required?
- What are the pressure conditions?
- What is the temperature range?
Step 2: Choose Port Configuration
| If You Need To… | Choose |
|---|---|
| Simply turn flow on/off | 2-way valve |
| Divert flow or control single-acting cylinder | 3-way valve |
| Control double-acting cylinder | 4-way valve |
| Independent exhaust speed control | 5-way valve |
Step 3: Select Default State
| If System Should… | Choose |
|---|---|
| Fail closed for safety | Normally Closed (NC) |
| Fail open (cooling, venting) | Normally Open (NO) |
| Flexible requirements | Universal |
Step 4: Determine Operating Type
| If Your System Has… | Choose |
|---|---|
| Low/zero pressure, small flow | Direct acting |
| Consistent minimum pressure, high flow | Pilot operated |
| Variable pressure conditions | Semi-direct |
Step 5: Match Materials
- Brass: General purpose, water, air, oil
- Stainless steel: Corrosive fluids, food grade, high temperature
- Plastic (PVC, PVDF): Aggressive chemicals, ultrapure water
- Seals: Match to fluid compatibility and temperature
Solenoid Valve Symbols
Understanding solenoid valve schematic symbols is essential for reading circuit diagrams.
Basic Pneumatic Solenoid Valve Symbols
2/2 Solenoid Valve (2 ports, 2 positions):
┌───┬───┐
│ ╱ │ │
────┤ │ ├────
│ │ ╲ │
└───┴───┘
▲
█ ← Solenoid actuator
3/2 Solenoid Valve (3 ports, 2 positions):
┌───┬───┐
┌─┤ ╲ │ ─ ├─┐
│ │ │ │ │
──┼─┤ ─ │ ╱ ├─┼──
│ └───┴───┘ │
└─────┬─────┘
▼
Exhaust
Symbol Components
| Symbol Element | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Rectangle boxes | Valve positions |
| Arrows | Flow paths when in that position |
| T symbols | Blocked ports |
| Rectangle with diagonal | Solenoid actuator |
| Zigzag line | Spring return |
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Installation Best Practices
- Mount correctly: Most valves work best in specific orientations—check manufacturer guidelines
- Use strainers: Install upstream filters to prevent debris damage
- Verify flow direction: Arrow on valve body indicates flow direction
- Allow for heat: Coils generate heat—ensure adequate ventilation
- Protect from moisture: Use appropriate IP-rated valves for wet environments
- Support piping: Don’t let valve support pipe weight
Common Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Valve won’t open | No power, burned coil, debris in orifice | Check power, test coil, clean valve |
| Valve won’t close | Debris preventing seal, worn seal, weak spring | Clean, replace seals or spring |
| Slow response | Low voltage, contamination, wrong valve type | Check voltage, clean, verify selection |
| Coil overheating | Wrong voltage, duty cycle exceeded, inadequate ventilation | Match voltage, check duty rating, improve airflow |
| Leaking | Worn seals, damaged seat, over-pressure | Replace seals, check pressure rating |
| Chattering/buzzing | AC coil issues, low pressure (pilot operated) | Check coil, verify minimum pressure |
Maintenance Schedule
- Weekly: Visual inspection for leaks
- Monthly: Check electrical connections
- Quarterly: Test operation, clean strainers
- Annually: Replace seals and inspect internals
Solenoid Valve vs Other Valve Types
| Feature | Solenoid Valve | Motorized Ball Valve | Pneumatic Valve |
|---|---|---|---|
| Response time | Very fast (10-50ms) | Slow (seconds) | Fast |
| Power source | Electrical | Electrical | Compressed air |
| Position control | On/off only | On/off or modulating | On/off or modulating |
| Fail position | Spring return | Stays in place | Configurable |
| Best for | Fast switching, automation | Large flow, throttling | High-speed industrial |
Conclusion
A solenoid valve is an essential automation component that uses electromagnetic force to control fluid flow quickly and reliably. Whether you’re designing an irrigation system, building industrial machinery, or working on automotive applications, understanding solenoid valve types and operating principles helps you select the right valve for reliable, efficient operation.
Key takeaways:
- Solenoid valves use electromagnetic coils to move a plunger that opens or closes flow
- Choose between direct acting (low pressure/flow) and pilot operated (high pressure/flow) based on your system
- Port configuration (2-way, 3-way, 4-way) determines control capability
- Default state (normally open vs normally closed) affects fail-safe behavior
- Match materials to your fluid, pressure, and temperature requirements
With the right solenoid valve properly installed, you’ll have precise, automated flow control that operates reliably for years.
Need help selecting the right solenoid valve? Contact our engineering team for expert assistance with valve sizing and specification.